Most of us rely on the refrigerator fully when it comes to preserving food and maintaining its freshness. So why not understand the intricate mechanisms that work for this cooling process? After all, learning these can actually save you great expenses and repairs or replacements in the future.
If you have adequate knowledge, you are definitely going to save your money because you will have a keen idea of what has gone wrong in your refrigerator.
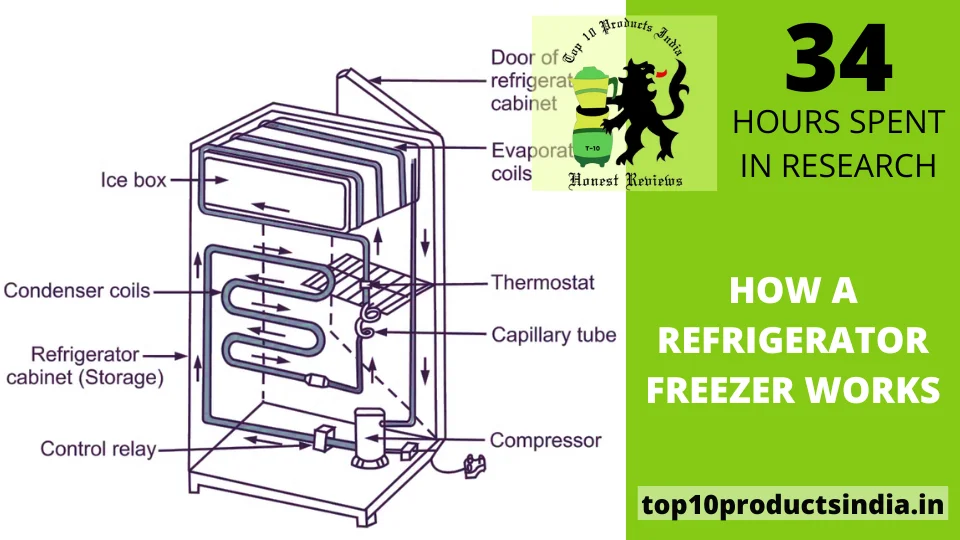
From the Inside Out: The Components of a Freezer
- Body: The body of a freezer is pretty much like the human body, with various parts playing their specific roles.
- Compressor: It is the heart of the freezer that pumps refrigerant through the system, and if it stops working, your refrigerator will stop cooling down the food.
- Condenser coils: These coils’ main job is to release heat from the refrigerant evaporator coil. The evaporator coil absorbs heat from within the freezer, where cooling magic takes place.
- Evaporator Coils: This regulates the flow of refrigerant gas into the evaporator, which completes the cooling process.
- Thermostat: This is like the brain of the freezer, which plays the role of maintaining the perfect temperature. It fully controls the refrigeration cycle.
The Science of Chill: How Your Freezer Keeps Things Frozen
- Heat removal: The freezer keeps things frozen by removing heat from the inside of your refrigerator.
- Refrigerant roll: Refrigerant is actually a special fluid that absorbs and carries the unwanted heat away to maintain coolness inside.
- The consistent cycle: It comprises three major practices, which are compression, condensation, and expansion. After these, the most important one takes place, which is evaporation, and that’s how the freezer maintains a perfect cold temperature without any disturbance.
- End goal: The final target is to create a perfect environment that preserves your food but doesn’t spoil it by over-freezing it or letting it spoil by offering less cold.
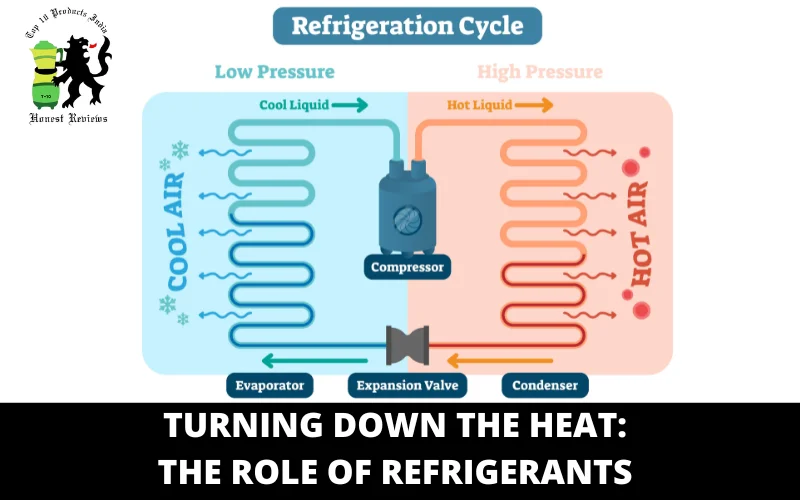
A Cool Journey: The Refrigeration Cycle Explained
First of all, comes the compressions in which the refrigerant starts as a gas. The compressor, which is the heart of the refrigerator, pressurizes it to raise its temperature. Then, condensation takes place, in which hot pressurized gas is moved through the condenser coils and thrown out of the freezer, where it loses its heat because of the surrounding cold air. This, at last, condenses into a liquid.
After that expansion takes place, where the liquid refrigerant passes through a sleek expansion valve, depressurization takes place, and it cools down quickly. The second and last part of this process is that this depressurized liquid enters the evaporator coils inside your freezer, where it absorbs heat from inside the freezer and cools it down.
Finally, the cycle keeps repeating itself again and again. That’s how your freezer maintains a perfect cold temperature within.
Turning Down the Heat: The Role of Refrigerants
Refrigerants play a bigger role than you think. Cooling systems, however, have some environmental impact. Not all of them, but yes, a few of them cause ozone depletion, as was taught to us in school time. These include HCFCs and CFCs.
However, with the evolution of science, now less impactful refrigerants have been invented. HFCs are a great example. However, we cannot say that HFCs don’t contribute to global warming.
So, we are shifting towards something more environmentally friendly, such as natural refrigerants like CO2, ammonia, and hydrocarbons. When we compare these to the gases mentioned before, they create very little tension in the ozone layer and are more energy efficient as well.
Refrigeration technology is evolving very fast, and in the future, we can expect it to offer zero percent damage to our environment.
Frost-Free Technology: Say Goodbye to Manual Defrosting
We all know how hectic manual defrosting can be. There is a lot of water pouring outside of the refrigerator. We have to clean it with clothes, and that’s a lot of hassle.
Now, you have the frost-free technology in refrigerators that actually eliminates the process of manual defrosting. Now, what’s with the traditional manual defrost? Their frost used to build up inside freezers, and if you didn’t do your manual defrosting on time, it not only led to energy inefficiency but also created problems for various food items kept inside.
Today’s technology has automatic defrost cycles, which prevent ice from gathering. Hence, you enjoy optimal cooling efficiency. So, the time and effort of the consumer are clearly saved, and food preservation is at its ultimate best.
Also, as there is no frost, the appliance consumes less energy, contributing to both short and long-term sustainability.
Efficiency in the Cold: How Modern Freezers Save Energy
- Insulation advancement minimizes energy loss by reducing heat transfer.
- The cooling process is quicker and less energy-consuming. Thanks to the energy-efficient compressors. No ice build-ups now and no extra surges in the electricity bills.
- Thanks to frost-free technology, which eliminates the energy-intensive defrost cycles.
- Traditionally, incandescent bulbs were used inside the refrigerator. But now we have LED lighting, which consumes much less energy.
- Many modern-day models come with a freezer containing special controls and smart temperature sensors that maintain perfect cooling levels automatically. So there is no energy wastage.
Temperature Control: Keeping Your Frozen Foods Just Right
- Temperature regulation is never an issue, thanks to the smart thermostats.
- There are some adjustable shelves and compartments for a perfect organization of airflow.
- If there are any temperature fluctuations, you have door alarms as well.
- To preserve the freshness of your food, a few freezers do have fast-freezing options for cooling newly added food items in no time.
- Many models come with freezers that provide some tremendous features, such as vacation mode. It conserves energy when the freezer isn’t in daily use.
Maintenance Tips: Keeping Your Freezer in Top Shape
- Never feel lazy in cleaning the interiors of your freezer to ensure perfect airflow.
- Door seals might create problems even if slightly damaged. So repair them before it’s too late.
- Whenever you feel like ice build-up has taken place more than natural, either you defrost your freezer manually or, if the automatic feature is present, then use it. Don’t overburden your freezer, which I mean. Just organize your food items properly so that air circulation takes place as needed.
- Vacuum the condenser coils every single year to remove debris and dust, which can create allergies.
- There must be adequate ventilation around the freezer so that there is nothing like overheating.
Troubleshooting Common Freezer Issues
Check out the obstructions blocking airflow vents in case you feel like your freezer isn’t cooling the way it is supposed to. If there is more frost build-up than normal, then the problem is with the door seals. If you check out and find some damage, don’t waste time and get it fixed as soon as possible.
If your freezer is generating more noise than normal, then the culprit is the evaporator fan motor. The water leakage problem is caused by issues in the drain line. There can be some clogs which you need to take care of.
FAQs
How does a refrigerator freezer maintain cold temperatures?
Well, it just circulates refrigerant gas through coils and then absorbs heat from inside. Later on, it releases it outside.
What role do refrigerants play in the cooling process of a refrigerator freezer?
Refrigerants such as R134a face compression and expansion cycles where they absorb heat inside the freezer and later release outside.
Is it possible to adjust the freezer temperature? If yes, then how?
Well, obviously, the straight answer is yes. Freezer compartments do have temperature controls. Even the old models too have it. So you can adjust it to your preference.
How often should I defrost my refrigerator freezer?
Well, it depends upon you. I’d recommend you do it once every 2 -3 months.