One of the most important parts of an average household appliance, such as a washing machine, is the motor. Today’s washing machines use a range of motors, including regular AC induction-specific designs such as brushless DC motors.
For example, depending on the type of motor one could decide to purchase and install into his/her washing machine, there are different types of motors in the market that power different brands of washing machines compared to old models with higher levels of cleaning efficiency than past machines.
Variable Speed Motors
Presently, Variable Speed Motors in Washing Machines Turn Out to Be the Market Standard. The other issue is that these motors are energy efficient compared to many others; this, therefore, makes them consume less power, thus saving clients on bills.
In addition, Variable Speed Motors have other properties that change some parameters and regulate them with a view to different requirements when washing clothes. The machine has a precision program by which you can wash with different speeds, like delicate or strong, depending on what the specific need is for the laundry.
Plus a win-win situation for energy conservation in minimizing excessive consumption, which is costly to consumers and an unfortunate trend for the environment.
What are the benefits of variable-speed motors?
- Reduced energy consumption– Variable speed motors consume about 40% less energy than fixed speed motors by their load sizes.
- Lower noise levels-Variable speed motors do not produce high noise levels, unlike conventional speed motors, which are very noisy.
- Greater flexibility-Variable speed motor machines enable the user to program several wash cycles according to the fabric type and load on them.
- Increased efficiency -More Energy Savings! Variable-speed Motors + Inverters.
What are the drawbacks of Variable Speed Motors?
- Cost –They turn out to be more costly than others.
- Complex Control System-The control of the motor at different speeds requires an elaborate and expensive control system.
- High Maintenance – With rapid speed changes, variable speed motors need constant maintenance because it leads to wear.
- Increased efficiency- Rapidly increasing or decreasing acceleration creates higher heat levels in variable-speed motors.
Brushless DC Motors
Because of their high reliability, brushless Direct Current motors for washing machines are the best and most effective form of electric motor. Unlike the typical brushed motor, this does not require regular checkups or repairs.
The two major benefits associated with a brushless DC motor include lower operating costs and enhanced energy efficiency. These are some of the reasons why they are smaller, quieter, more reliable, and do not need oiling as much as brushed motors.
Brushless DC motors in washing machines can offer higher acceleration, better performance, prolonged service life, and reduced power consumption more than conventional DC motors. They are used globally for laundry purposes for this reason.
What are the benefits of Brushless DC Motors?
- Increased efficiency -Brushless DC Motors are approximately 30% more efficient than ordinary motors.
- Greater control DC Motors give good control on speed and torque, allowing you to get high-performance results every time in cyclic processes.
- Quieter operation-Being brushless, these motors are by nature quieter than conventional motors.
- Longer-lasting performance result was a brush-free DC motor – which delivered substantially longer-lasting service life than its counterparts.
What are the drawbacks of Brushless DC Motors?
- The high initial cost of these brushless DC motors is generally expensive and, hence, unaffordable in other applications.
- Complex maintenance-Brushless DC motors need complex maintenance since they lack commutators and brushes.
- Sensitivity to temperature changes: DC motors are sensitive to temperature changes since they have no surrounding air movement.
- Vibration levels can be high-High vibration levels may exist due to high speed and magnetic field instability.
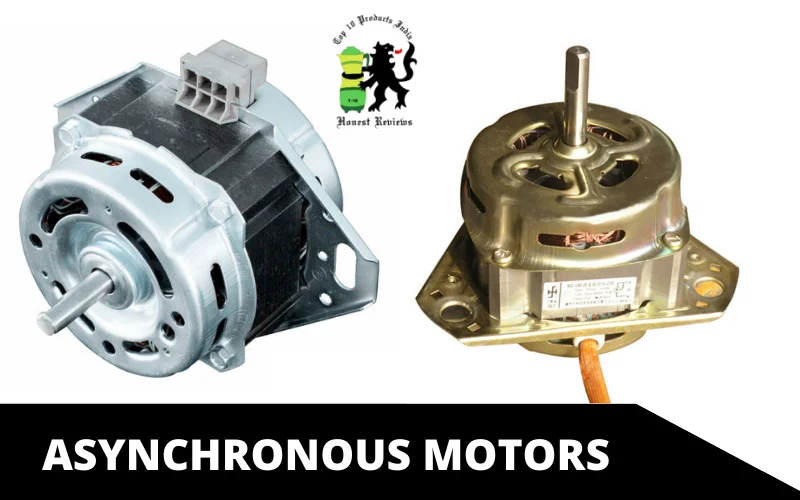
Asynchronous Motors
The most common motor for washing machines is an asynchronous motor, also known as an induction motor. This washer utilizes rotating magnetic fields that spin the cylindrical drum inside the washer at an effective speed and torque sufficient to clean the clothes properly.
The two fundamental components of an asynchronous motor include a stator and an inner coil of wires producing the oscillating magnetic field.
These motors have gained popularity for being used in washing machines as they do not require mechanical gears or brushes, making them economically efficient. Moreover, these are also very low maintenance, so apart from switching on/off, changing the laundry soap is all they need.
What are the benefits of Asynchronous Motors?
- Improved efficiency – Asynchronous motors may decrease the energy expenditure of such motors’ conventional counterparts by as much as 10%.
- Smoother start-up operation- Unlike synchronous motors that have to start quickly and stop, asynchronous motors are geared towards gentle acceleration and deceleration, making them better suited for heavy-load washing machines.
- Quieter The first advantage of asynchronous motors is that they can minimize the noise generated during operation since there is no rotor-to-stator direct contact.
- Often, effective – Asynchronous motors are generally cheaper due to their simple design compared to other motor types.
What are the drawbacks of Asynchronous Motors?
- Low starting torque– It takes a large current to initiate an asynchronous motor compared to other types of motors.
- Motor speed depends on frequency-Frequency-controlled drives are unsuitable for use with asynchronous motors since motor speed depends on frequency.
- Vibration and noise levels can be high-Synchronous motors have high rotational speeds that may result in Vibration and Noise.
- Power factor decreases with higher speed- The power factor declines due to efficiency lost in motors.
Universal Motors
The motor of a washing machine is a universal electrical type, which allows utilizing AC or DC supplies for its operation. The special characteristic presents it as very mobile and highly affordable.
The universal motor has two windings that are divided into windings of a DC source and windings of an AC source. The two windings meet at this point, forming a strong magnetic field that drives the movement of the inner drum.
This has made washing machines small but able to wash larger loads faster than before.
What are the benefits of Universal Motors?
- Low price-The universal motor is one of the cheapest motors around.
- Ability to run on any AC/DC power source – universal motor runs on AC or DC power without distinction of alternating and direct voltages.
- Compact size-Universal motors are well suited to be used in compact washing machines because of their compact size.
- Power and speed control-Universal motors provide good cleaning process control through speed and power adjustment.
What are the drawbacks of Universal Motors?
- Loud operation – Universal motors are louder in their operations as the rotor and stator operate in direct contact with each other compared to other motor types.
- Low efficiency – Universal motors are wasteful of energy as heat and, therefore, have a lower efficiency compared to other motors.
- Unpredictable performance – Universal motors are unreliable at maintaining steady speed and torque levels; hence, their performance could be unpredictable in a washing machine.
- Limited control – Being without feedback mechanisms in a universal motor makes it difficult to control aspects like current, voltage, and speed.
Conclusion
Ultimately, it is up to application requirements, cost, and user’s taste to decide which motor should be mounted on a washing machine.
The efficiency of brushless DC Motors is high, but the initial cost for them is greater, while the cost of variable speed motors is relatively higher. These motors need regular maintenance.
In case basic applications are concerned, standard AC motors can become quite affordable and easy to operate. For instance, various motors have their own merits and demerits that should be considered before determining which motor suits an application.